Abstract
Background: c-MYC is a transcription factor that promotes oncogenesis by activating and repressing its target genes that control cell growth, metabolism, and proliferation. MYC is deregulated in a large proportion of aggressive B-cell lymphomas. A typical example is the Double-Hit Lymphoma (DHL) and Double-Expression Lymphoma (DEL) which present with a rapidly progressing clinical course, refractory to treatment, poor clinical outcome, and currently considered incurable. Nevertheless, MYC is considered as an "undruggable" target since it has no "active site" amenable to binding by conventional small molecule inhibitors. Moreover, MYC has a broad spectrum of functions in cell proliferation, survival, metabolism, and others, so direct inhibition would likely cause severe side effects. Besides direct inhibition, another practical strategy is to target druggable proteins that are essential for the viability of MYC-driven tumors, inducing MYC-dependent "synthetic lethality". The advantage of such approach is a capability of killing tumor cells discriminately, while leaving non-tumor cells intact or less influenced. This study is designed to identify such targets and explore practical novel strategies to treat MYC-driven lymphomas, especially DHL/DEL.
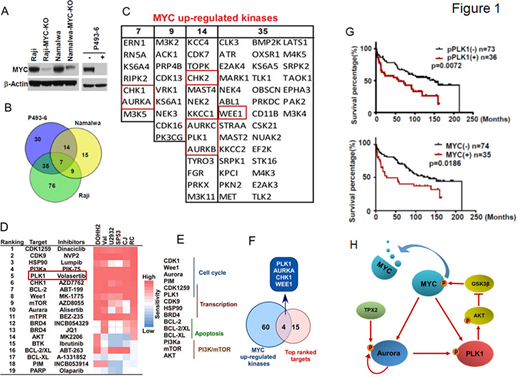
Methods and Results: By integrating activity-based proteomic profiling and drug screens in isogenic MYC on/off lymphoma cells, we identified polo-like kinase-1 (PLK1) as an essential regulator of the MYC-dependent kinome in DHL/DEL. Notably, PLK1 was expressed at high levels in DHL, correlated with MYC expression and connoted poor outcome. Further, PLK1 is directly activated by MYC on transcriptional level and in turn, PLK1 signaling augmented MYC protein stability by promoting its phosphorylation and suppressing its degradation. Thus, MYC and PLK1 form a feed-forward circuit in lymphoma cells. Finally, both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that inhibition of PLK1 triggered degradation of MYC and of the anti-apoptotic protein MCL1, and PLK1 inhibitors showed synergy with BCL-2 antagonists in blocking DHL/DEL cell growth, survival, and tumorigenicity. These data support that PLK1 is a promising therapeutic target in MYC-driven lymphomas.
Brief summary: Functional pharmacoproteomics identified PLK1 as a therapeutic vulnerability for MYC-driven lymphoma, which was a synthetic lethal for DHL/DEL when targeted with BCL-2 inhibitors.
Vose:Roche: Honoraria; Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Epizyme: Honoraria; Legend Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Celgene: Research Funding; Incyte Corp.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal